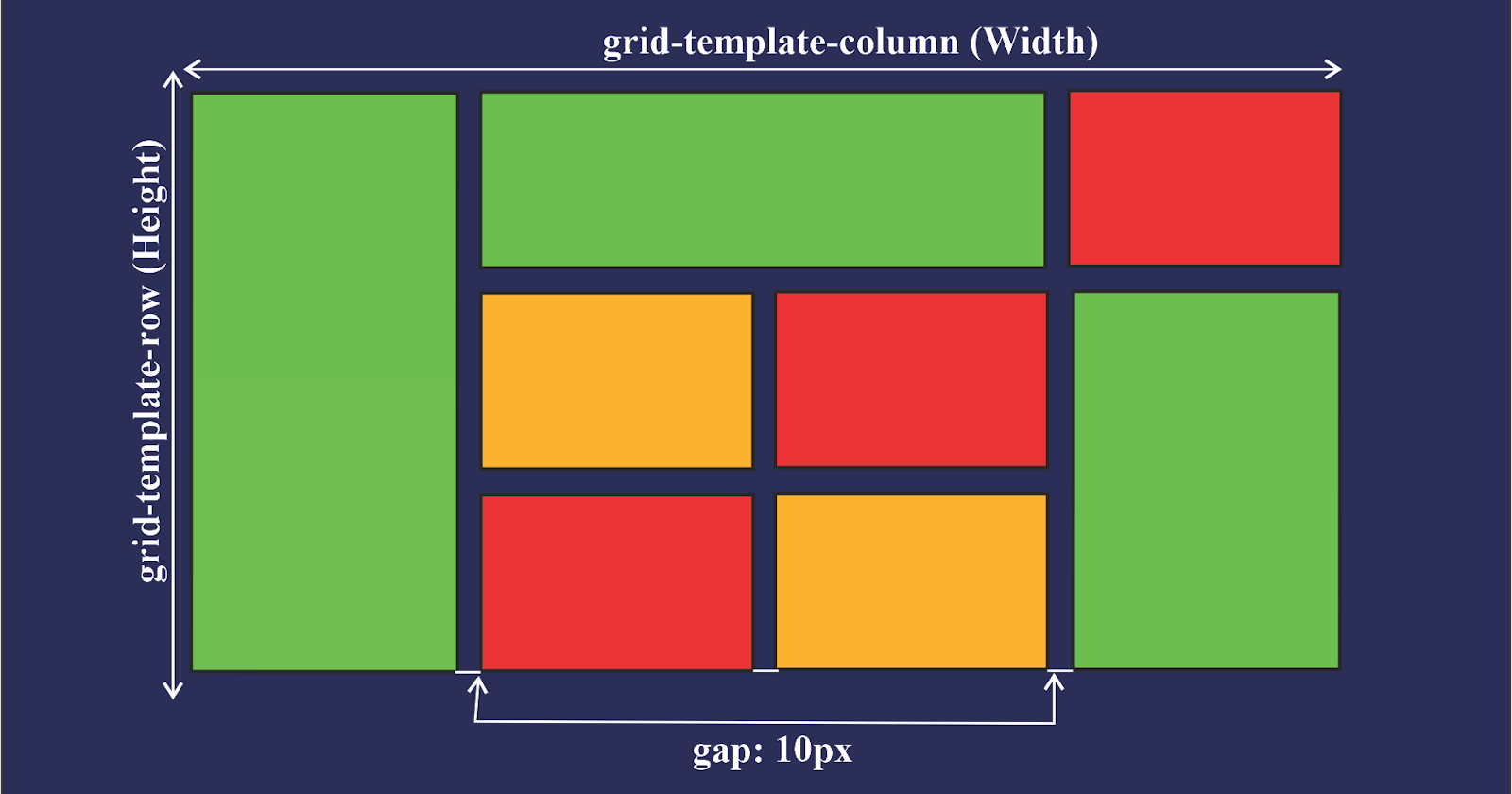
Grid Layout enables you to divide a page into major regions or define the relationship between parts of a control using HTML primitives in terms of size, position, and layer.
Grid layout allows an author to align objects into columns and rows similar to tables. But with CSS grid, many more layouts are either feasible or simpler than they were with tables. For instance, like CSS-positioned components, the child elements of a grid container could position themselves so that they truly overlap and layer.
Features of CSS Grid Layout:
Flexible Track Sizes
You can use the Fraction Unit to assign any specified pixel value to the grid. This will make your grid organized and responsive.
Item Placement
CSS grid has made it much easier to position items in the container in any area you want them to be without having to mess with the HTML markup.
Alignment Controls
The alignment of an item in a container is easier than ever before with CSS Grid. In the container, you can now arrange items horizontally and vertically as you wish.
The benefits of CSS grids:
CSS Grids are very flexible and responsive, make it easy to create two-dimensional layouts, and are compatible with most web browsers.
By using CSS grids, your mark-up (HTML code) is cleaner (and you have more flexibility). This is partly because you don't have to change the mark-up (HTML code) to change the position of an item. With CSS Grid Layout, we can build more complex layouts using both columns and rows.
When Should You Use CSS Grid:
Although you can use CSS Grid in practically any aspect of web development, there are certain situations when it's ideal.
For example, when we have a complex design layout to implement, CSS Grid is better than the CSS float property. This is because Grid is a two-dimensional layout, whereas the CSS float property is a one-dimensional layout.
Grid is also a good choice when we need space or gap between elements. By using the CSS grid gap property, the spacing of two elements is much easier than using the CSS margin and padding properties which might end up complicating things.
CSS Grid Properties:
The CSS grid layout consists of many grid properties. Now we'll take a look at some of them so we can learn how to use them:
Grid container property
This is a CSS grid property that houses the grid items/elements. We implement the CSS grid container property by setting the container to a display property of grid or in-line grid.
For Example:
display: grid;
or
display: in-line grid;
Grid-template-column property
This is a property used to set each column’s width. It can also define how many columns you want to set for your project.
For Example:
grid-template-column: 100px auto 100px;
Grid-template-row property
You use the CSS row property to set the height of each column. You can also use it to define how many rows you want to set in your project.
You can implement the CSS gird row property using grid-template-row, like this:
grid-template-row: 50px 50px;
For example:
grid-template: 50px 50px / 100px auto 100px;
Column-gap property
As the name states, it is a grid property that assigns a space between two or more columns in a container. You can do this by using the column-gap property and giving it value. For example:
column-gap: 20px;
From the code above, you can see that a gap of 20px was assigned to the column.

Row-gap property
Just like column-gap, row-gap is a CSS property that assigns a space between two or more rows in a container. For example:
row-gap: 50px;
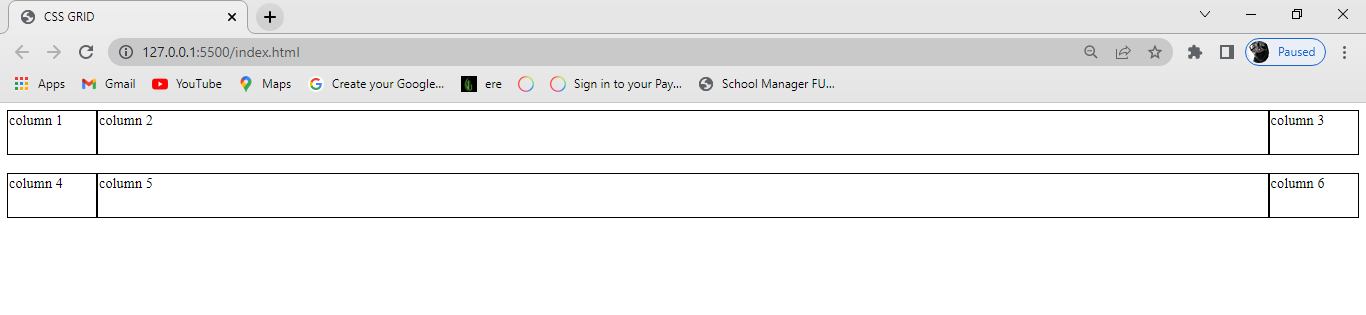
Justify-content property
This is a grid property that you use in positioning items (columns and rows) horizontally in a container. It displays how the web browser positions the spaces around the items (columns and rows).
The justify-content property has six possible values:
Startendcenterspace-aroundspace-betweenspace-evenly
Start:
This positions the items at the left side of the browser and can be executed with the following code:
justify-content: start;
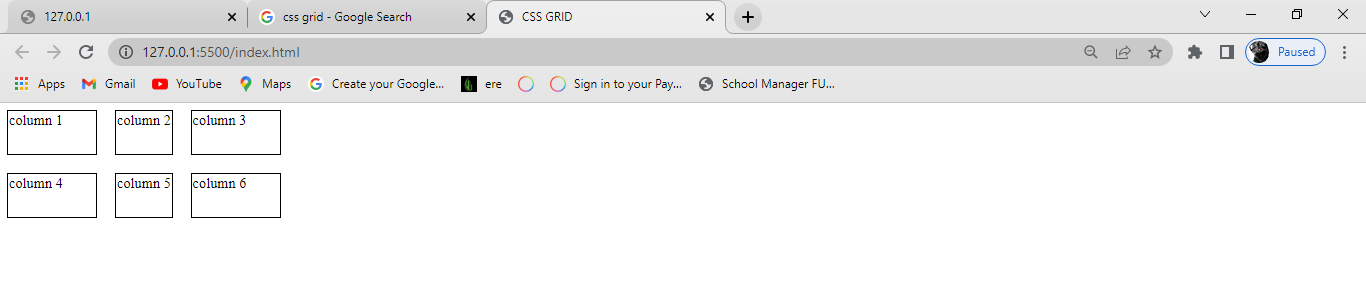
End:
This positions the items on the right side of the browser and can be executed with the following code:
justify-content: end;

Center:
This positions the items at the center of the browser and can be executed with the following code:
justify-content: center;

Space-around:
This property distributes the items in the container evenly, where each item in the container has an equal amount of space from the next container.
justify-content: space-around;
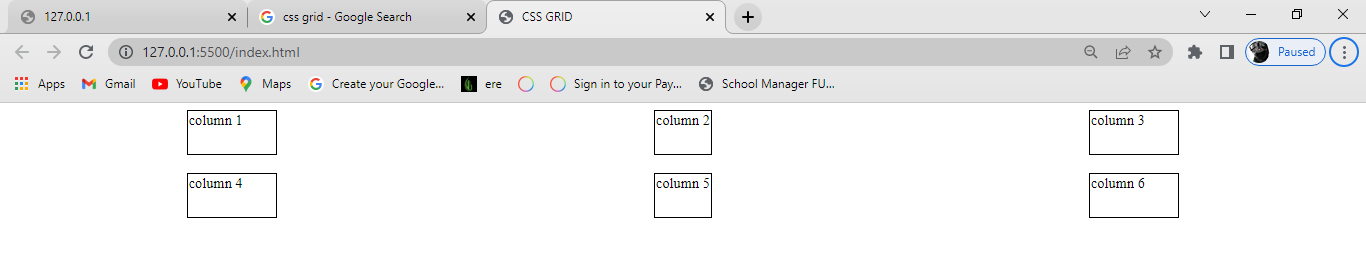
Space-between:
Just like the space-around property, space-between distributes the items in the container evenly, where each item in the container has an equal amount of space from the next one in the container. It takes up the entire width of the container.
justify-content: space-between;
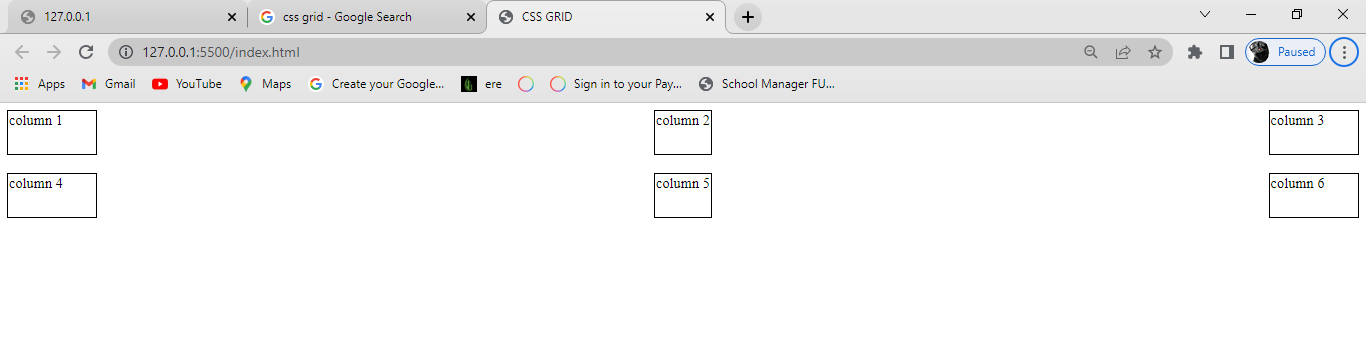
Space-evenly:
Just as the name states, this property distributes the items in the container evenly, where each item in the container has an equal amount of space from the next one in the container.
justify-content: space-evenly;
Align-content property
Align-content is the opposite of justify-content. You use the align-content property in positioning items vertically in a container.
Just like justify-content, the align-content property has six possible values:
Startendcenterspace-aroundspace-betweenspace-evenly
Start
This positions the items at the top of the browser and can be executed with the following code:
align-content: start;

End
This positions the items at the bottom of the browser and can be executed with the following code:
align-content: end;

Center
This positions the items at the center of the browser and can be executed with the following code:
align-content: center;
Space-around
This property distributes the items along the side of the container evenly, where each item in the container has an equal amount of space from the next one vertically.
align-content: space-around;

Space-between
Just like the space-around property, Space-between distributes the items in the container evenly, where each item in the container has an equal amount of space from the next one in the container, and takes up the entire width of the container in the vertical direction.
align-content: space-between;

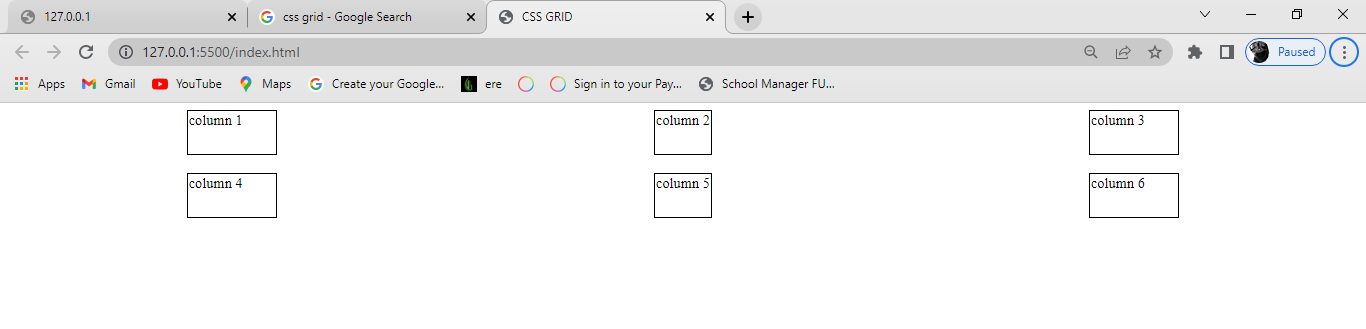
Space-evenly
Just as the name states, this property distributes the items in the container evenly, where each item in the container has an equal amount of space from the next one vertically.
align-content: space-evenly;
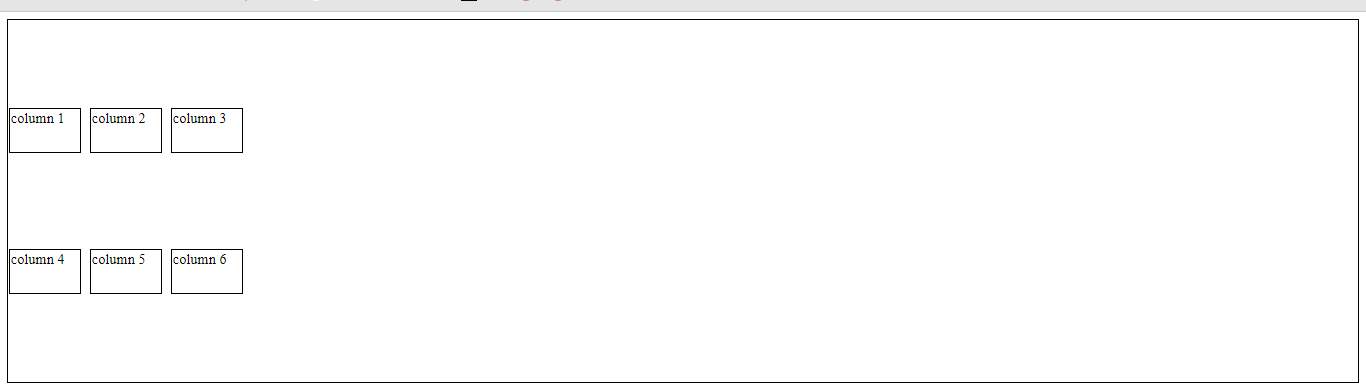
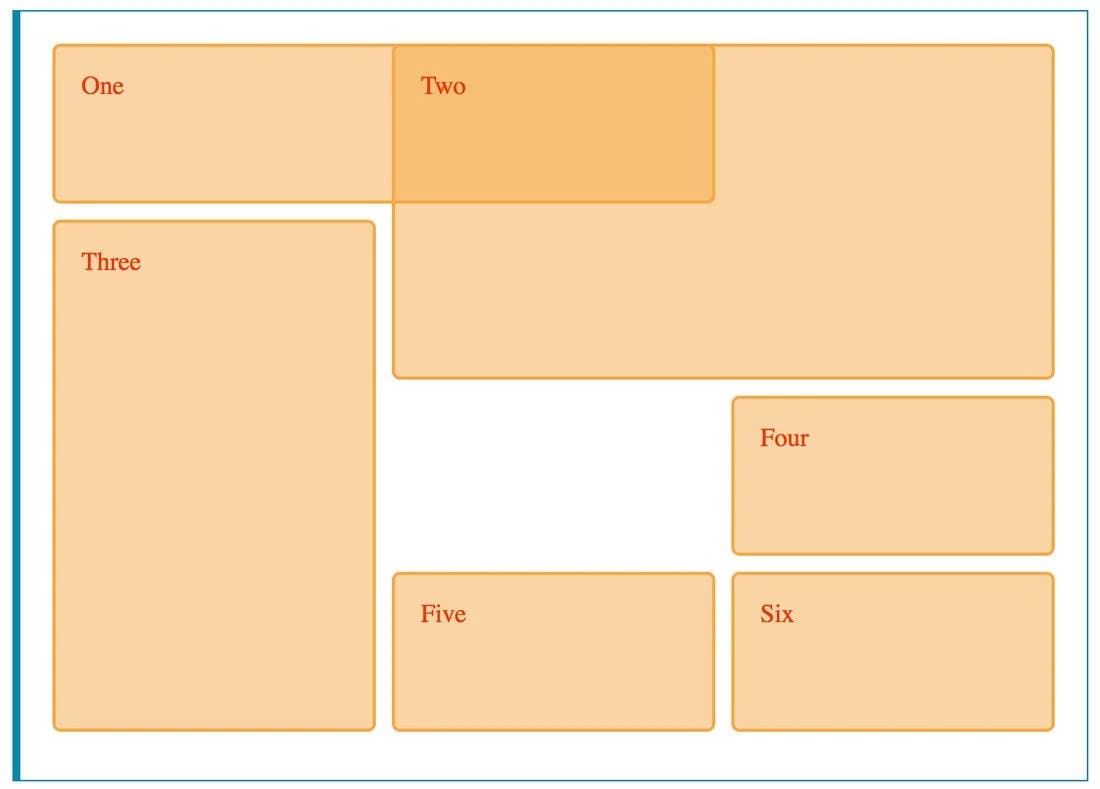
Basic example:
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="one">One</div>
<div class="two">Two</div>
<div class="three">Three</div>
<div class="four">Four</div>
<div class="five">Five</div>
<div class="six">Six</div>
</div>
.wrapper {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: repeat(3, 1fr);
gap: 10px;
grid-auto-rows: minmax(100px, auto);
}
.one {
grid-column: 1 / 3;
grid-row: 1;
}
.two {
grid-column: 2 / 4;
grid-row: 1 / 3;
}
.three {
grid-column: 1;
grid-row: 2 / 5;
}
.four {
grid-column: 3;
grid-row: 3;
}
.five {
grid-column: 2;
grid-row: 4;
}
.six {
grid-column: 3;
grid-row: 4;
}
Output:
Functions
Data types