Table of contents
Hyper Text Markup Language describes the structure of a Web page, containing a series of elements. HTML elements tell the browser how to display the page.
In this article, we will know the HTML Elements, along with understanding the various available elements & their syntax through the examples. An HTML element is a component of an HTML document that tells a web browser how to structure and interpret a part of the HTML document. HTML elements can contain formatting instructions, semantic meaning, and content.
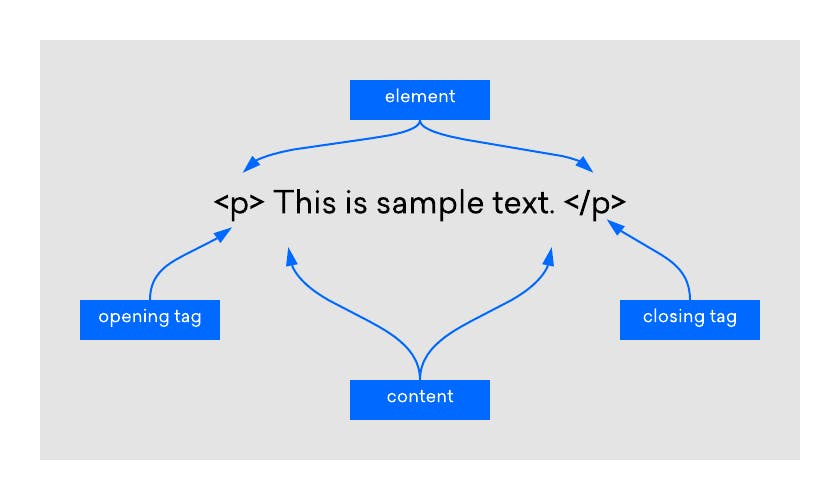
Technically, an element is a collection of start tags, attributes, end tags, and content between them.
Syntax:
<tag name>content</tag name>
If there is no content within an HTML element, it is known as an Empty tag, for example, <br>(line break), <hr>(horizontal rule),<link>,<input>,<img> etc. These elements are also called as unpaired tags and void elements.
Nested HTML elements: HTML can be nested, which means an element can contain another element
For the default display and styling purpose in HTML, all the elements are divided into two categories:
Block-level element
Inline element
Block-level elements:
These are the elements, which structure the main part of a web page, by dividing a page into coherent blocks.
A block-level element always starts with new line and takes the full width of a web page, from left to right.
These elements can contain block-level as well as inline elements.
Following are the block-level elements in HTML.
<address>, <article>, <aside>, <blockquote>, <canvas>, <dd>, <div>, <dl>, <dt>, <fieldset>, <figcaption>, <figure>, <footer>, <form>, <h1>-<h6>, <header>, <hr>, <li>, <main>, <nav>, <noscript>, <ol>, <output>, <p>, <pre>, <section>, <table>, <tfoot>, <ul> and <video>.
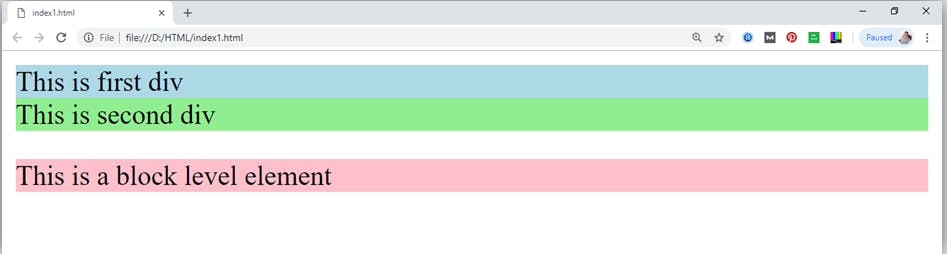
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<div style="background-color: lightblue">This is first div</div>
<div style="background-color: lightgreen">This is second div</div>
<p style="background-color: pink">This is a block level element</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Inline elements:
Inline elements are those elements, which differentiate the part of a given text and provide it with a particular function.
These elements do not start with a new line and take width as per requirement.
The Inline elements are mostly used with other elements.
<a>, <abbr>, <acronym>, <b>, <bdo>, <big>, <br>, <button>, <cite>, <code>, <dfn>, <em>, <i>, <img>, <input>, <kbd>, <label>, <map>, <object>, <q>, <samp>, <script>, <select>, <small>, <span>, <strong>, <sub>, <sup>, <textarea>, <time>, <tt>, <var>.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<a href="https://www.javatpoint.com/html-tutorial">Click on link</a>
<span style="background-color: lightblue">this is inline element</span>
<p>This will take width of text only</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:

Summary:
In this article, we’ve seen the difference between the basic definition of HTML elements. We’ve gone through some of the basic HTML elements to carry out tasks.
